Hemorrhoids/Treatment
Hemorrhoids are swollen veins that develop in the anus or lower rectum. At some time in our lives, almost 75% of people will experience symptomatic hemorrhoids.
Why hemorrhoids enlarge and require treatment is largely unknown but there are a variety of common factors that contribute to developing hemorrhoids:
- Chronic Constipation
- Pregnancy
- Childbirth
- Obesity
- Heavy Lifting
- Diarrhea
- Sitting on the toilet for long periods of time
- Weakened connective tissues associated with aging
- Low fiber diet
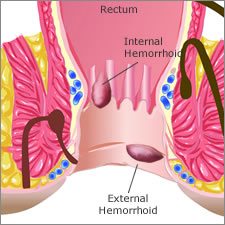
Hemorrhoids are classified based on their location, and are considered either internal hemorrhoids or external hemorrhoids. It is often difficult for patients to determine if a hemorrhoid is internal or external so it is important that you consult your gastroenterologist to obtain a proper diagnosis. Treatment options depend upon the type of hemorrhoid that has developed.
Internal Hemorrhoids
Internal hemorrhoids develop inside of the lower rectum. This type of hemorrhoid cannot be felt or seen, and is often painless. You may notice an internal hemorrhoid by seeing small amounts of bright red blood on toilet paper or in the bowl after a bowel movement. Sometimes you may experience a feeling of fullness around the rectum following a bowel movement.
Internal hemorrhoids can protrude through the anal opening. This is known as a prolapsing hemorrhoid. When an internal hemorrhoid protrudes through the anal opening the patient often experiences pain. Occasionally, prolapsed hemorrhoids spontaneously reduce, or go back inside the anal opening. In many situations the prolapsed hemorrhoids must be pushed back into the anus, or manually reduced.
Internal hemorrhoids could lead to the development of external hemorrhoids or skin tags, which is a build-up of excess skin. For most patients, the treatment of the prolapsed internal hemorrhoid will relieve the external discomfort associated with the hemorrhoid. Your gastroenterologist can provide you with detailed information about the treatment options available for internal hemorrhoids.
External Hemorrhoids
External hemorrhoids develop outside of the anal canal, and appear as bulges or lumps around the anus. External hemorrhoids are often painful due to the sensitive nerve fibers that are present in this region.
External hemorrhoids may bleed or itch, and often cause pain when the patient sits down. This type of hemorrhoid is less common than an internal hemorrhoid. Blood may pool in an external hemorrhoid, and this can form a blood clot referred to as a thrombosed hemorrhoid, which is often painful.
Your gastroenterologist can provide you with detailed information about the treatment options available for external hemorrhoids.
Treatment for Hemorrhoids
It is important to consult your gastroenterologist regarding any pain associated with hemorrhoids so that he can determine the type and severity of the condition. There are a variety of home remedies that are popular forms of hemorrhoid treatment, but these options usually offer only temporary relief from the symptoms of hemorrhoids. Popular forms of home treatment include warm sitz baths, suppositories and hemorrhoid creams. Consult your physician before pursuing any form of home treatment options.
Hemorrhoids can grow progressively worse over time, and for many people medical treatment such as hemorrhoid banding is necessary. If left untreated, hemorrhoids can grow in size.